WHAT IS ROBOTIC SURGERY
Robotic surgery is surgery using a robot. During robotic surgery, the surgeon is in front of a surgery 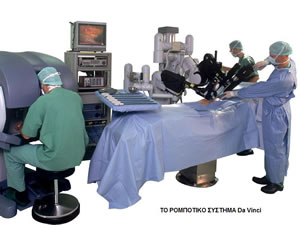 console-PC, where they see on a screen the surgical field in 3D and enlarged, and performs the operation by moving special control levers that look like joysticks.
console-PC, where they see on a screen the surgical field in 3D and enlarged, and performs the operation by moving special control levers that look like joysticks.
The commands given by the surgeon through the levers are digitally transferred, with remarkable precision, to the articulated arms of a surgical robot, which performs the movements on the surgical field. The robot’s movements are 100% controlled by the surgeon who must be specially trained in the use of robotic systems.
Robotic surgery is the evolution of endoscopic surgery. It is a minimally invasive and minimally traumatic surgical method, allowing the use of very small and flexible tools by the surgeon performing the surgical movements, with unprecedented precision through tiny incisions on the patient’s skin.
HOW ROBOTIC SURGERY WAS DEVELOPED
The first challenge of robotic surgery is related to telemedicine. Until today, performing remote  surgery, i.e. without the patient and the surgeon being at the same place, was unthinkable. This limitation led NASA and the military to initiate research programs to develop a way to perform surgery on astronauts by doctors on earth, and in the same manner on soldiers whose lives were at risk, by doctors that were at a remote and safe place! Thus, the need for telemedicine was born, and that set the foundations for the creation of robotic surgery.
surgery, i.e. without the patient and the surgeon being at the same place, was unthinkable. This limitation led NASA and the military to initiate research programs to develop a way to perform surgery on astronauts by doctors on earth, and in the same manner on soldiers whose lives were at risk, by doctors that were at a remote and safe place! Thus, the need for telemedicine was born, and that set the foundations for the creation of robotic surgery.
Another limitation that robotic surgery had to, and did, overcome are the limitations imposed by the design of laparoscopic tools, which were not flexible enough to make certain movements. By the overwhelming acceptance of laparoscopic surgery by the surgical community, because of the unique benefits it offers to the patients, it was necessary to overcome this limitation, as it eventually happened with the evolution of robotic surgery.
Robotic surgery allowed the elimination of the restrictions existing while operating in small and limited surgical fields. The unique precision of the surgical arms movement allows surgeons and paediatric surgeons to perform operations on body parts they would not dare to operate on in the past and save lives with the least possible risk.
WHICH SURGERIES CAN BE ROBOTICALLY PERFORMED
Robotic surgery is substantially the evolution of laparoscopic surgery, regarding the ergonomics of some tools.
As stated by all serious global studies, the main use of the method is in prostate surgery. There, the benefits are significant, mainly due to the preservation of the nerves of the erectile function.
In every day surgical operations, such as the removal of the gall bladder, the repair of hernias, the intestine, stomach, oesophagus, liver, pancreas, and thyroid surgeries, robotic surgery offers no additional benefits for the patient, compared to laparoscopic surgery, on the contrary its cost is significantly higher.
We are expecting new global scientific studies in the future, to precisely determine the place of the method in General Surgery procedures.
WHAT IS THE daVINCI SURGICAL SYSTEM
The daVinci Surgical System is the first robotic surgery system that is approved by the U.S. Food and 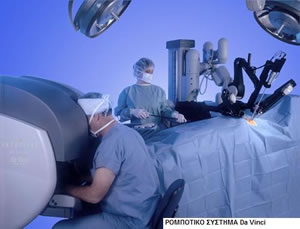 Drug Administration (FDA) for performing surgical operations.
Drug Administration (FDA) for performing surgical operations.
It consists of the surgeon’s console, where the surgeon is seated and, having on his screen an enlarged, 3D image of the surgical field, moves the special levers that drive the robot’s surgical arms. The robotic arms unit, where the surgical tools and the endoscope (camera) are, is placed next to the patient, a few meters away from the surgeon’s console. The surgeon’s team is also there.
The design of the daVinci surgical system began in 1995, and from 2000 till today it is used in more than 350 hospitals worldwide, while its use is recently rapidly spreading because of its significant advantages.
The pioneering daVinci robotic surgery system provides more precision and safety in everyday surgical operations. The development and adoption of robotic surgery makes the most hopeful scenarios for the future of medicine come true.
